Knee replacement surgery is usually recommended for individuals experiencing severe knee pain or damage that interferes with daily activities. The main reasons for surgery include advanced osteoarthritis, where cartilage wears down causing bone-to-bone friction; severe injury or trauma leading to joint damage; and rheumatoid arthritis or other conditions resulting in chronic inflammation and stiffness. When pain limits essential movements like walking or standing, exploring different types of knee replacement surgery can help restore mobility and improve quality of life.
Why is Knee Surgery Done?
Knee replacement surgery is typically considered for patients with severe knee pain or damage that affects daily life. The primary reasons for knee surgery include:
- Advanced Osteoarthritis: A common reason for knee surgery, where the cartilage wears down, causing painful bone-to-bone contact.
- Severe Injury or Trauma: Past injuries can lead to significant wear on the knee joint, making surgery necessary.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis or Other Conditions: Conditions that cause knee joint inflammation, pain, and mobility loss.
- Daily Life Impact: If knee pain affects basic activities like walking, bending, or standing, surgery becomes a suitable option.
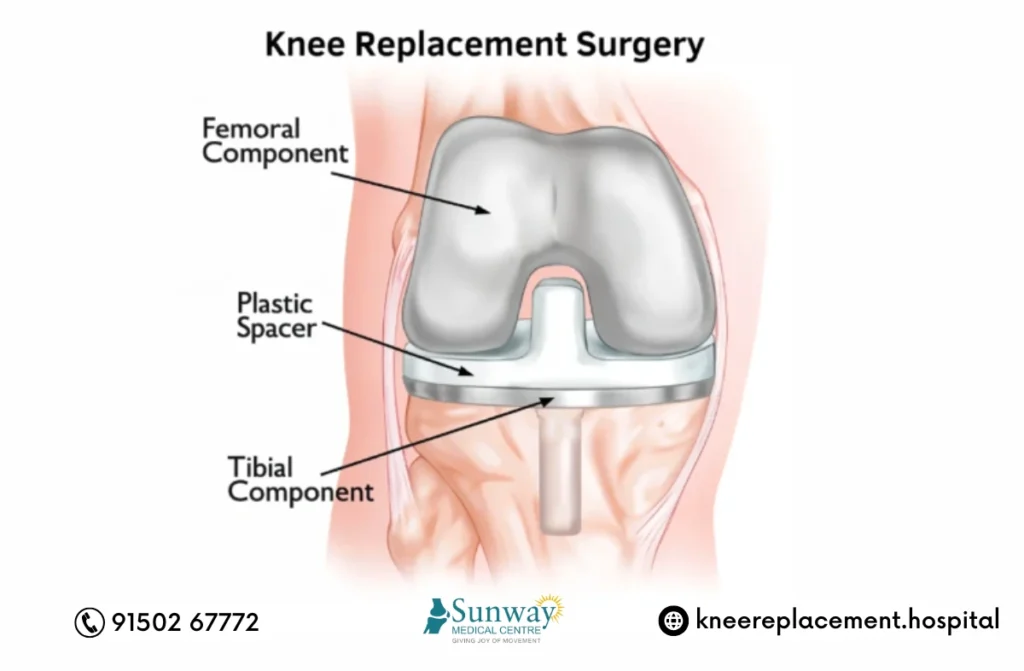
Latest Developments in Knee Replacement
In recent years, knee replacement surgery has seen remarkable advancements that have transformed patient outcomes. Robotic-assisted and minimally invasive techniques now allow for greater precision, reduced pain, and faster recovery. The materials used in artificial knee joints have also improved, minimizing complications and extending implant longevity. Depending on each patient’s needs and health condition, surgeons recommend the most suitable option among the different types of knee replacement implants, ensuring optimal comfort, function, and long-term success.
Different Types of Knee Replacements and Surgeries
Choosing the right procedure depends on the extent of knee damage, patient lifestyle, and the surgeon’s expertise. Understanding the best type of knee replacement helps ensure better outcomes and long-term comfort. Here’s a simple breakdown of the different types of knee replacement surgeries, each designed to relieve pain, improve movement, and restore daily function based on individual needs and medical conditions
- Total Knee Replacement: Involves replacing the entire knee joint.
- Partial Knee Replacement: Only a damaged part of the knee is replaced.
- Revision Knee Replacement: This is performed when a previous knee replacement fails or wears out.
- Bilateral Knee Replacement: Both knees are replaced during the same surgery.
- Patellofemoral Replacement: Focuses on the kneecap area specifically.
- Robot-Assisted Knee Replacement: Uses robotic technology to enhance precision during surgery.
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is among the most widely performed procedures for relieving severe knee pain and restoring mobility. It involves replacing the damaged joint surfaces with artificial components designed to mimic natural movement. The choice among different types of knee replacement implants depends on factors such as the patient’s age, bone quality, lifestyle, and overall health, ensuring the best long-term results and improved quality of life.
- Indications: It’s often recommended for patients with severe osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Procedure Details: The surgery typically lasts 1-2 hours and requires a hospital stay.
- Recovery Time: Full recovery may take several months, but many experience significant pain relief soon after.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Patients receive general or spinal anesthesia.
- Incision: A surgical incision is made over the knee.
- Bone Preparation: Damaged bone and cartilage are removed.
- Implantation: Artificial joint components are securely fixed in place.
Risks
- Infection: There’s a risk of infection at the surgical site.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots may form in the legs post-surgery.
- Implant Failure: In rare cases, the artificial joint may fail.
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement is a specialized procedure where only the damaged portion of the knee joint is replaced, preserving healthy bone and tissue. It offers quicker recovery and more natural movement compared to total replacement. Among the different types of knee replacement surgery, this option is ideal for patients with limited joint damage, providing effective pain relief and improved joint function while maintaining stability and flexibility.
- Indications: Suitable for patients with damage confined to one side of the knee.
- Advantages: Less invasive than total knee replacement, leading to quicker recovery times.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Patients receive anesthesia, similar to total knee replacement.
- Incision: A smaller incision is made compared to total knee replacement.
- Joint Replacement: Only the damaged area is removed and replaced.
Risks
- Limited Longevity: The lifespan of partial implants may be shorter than total replacements.
- Infection: As with any surgery, there’s a risk of infection.
- Knee Instability: Some patients may experience instability in the knee post-surgery.
Revision Knee Replacement
Revision knee replacement is performed when a previous knee replacement fails or causes complications. Understanding this new type of knee replacement surgery is crucial for patients who have undergone prior knee surgeries. Here’s what to know: best type of knee replacement Revision knee replacement is performed when a previous knee replacement fails or causes complications. Understanding this knee replacement surgery is crucial for patients who have undergone prior knee surgeries. Here’s what to know:
- Reasons for Revision: May include infection, wear and tear, or loosening of the implant.
- Outcomes: Patients often experience improved function after revision surgery.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Similar to initial surgeries, general or spinal anesthesia is used.
- Incision: A larger incision may be necessary to access the previous implant.
- Implant Removal: The old implant is carefully removed before placing a new one.
Risks
- Infection Risk: Higher risk due to the presence of previous implants.
- Complexity: More complex than initial replacements, leading to longer recovery.
- Uncertainty: Outcomes can vary based on the condition of the original joint.
Bilateral Knee Replacement
Bilateral knee replacement involves replacing both knees in a single surgical procedure, providing relief for patients with severe pain in both joints. Among the different types of knee surgery, this approach helps reduce overall recovery time and hospital visits. It allows simultaneous treatment, improving mobility and quality of life more efficiently. Patients benefit from coordinated care and faster return to daily activities compared to separate surgeries. Here are the important details:
- Benefits: Simultaneous surgery may reduce overall recovery time.
- Patient Selection: Ideal for patients with severe bilateral knee arthritis.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: General or spinal anesthesia is administered.
- Incision: Larger incisions are made on both knees.
- Joint Replacement: Both knee joints are replaced during the same operation.
Risks
- Increased Recovery Time: Recovery can be longer due to the nature of the procedure.
- Potential Complications: Risks include blood clots and infection.
- Rehabilitation Needs: Patients may need more intensive rehabilitation.
Patellofemoral Replacement
Patellofemoral replacement targets the kneecap and the underlying joint area, providing relief for localized damage. It is one of the different types of knee surgery and is ideal for patients with specific joint conditions. This procedure preserves healthy bone and tissue while improving mobility. Suitable candidates can experience reduced pain and faster recovery compared to total knee replacement. Here’s what you should know:
- Indications: Often recommended for patients with arthritis localized to the kneecap.
- Advantages: Less invasive than total knee replacement, preserving more healthy joint tissue.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Anesthesia is administered similar to other knee surgeries.
- Incision: A smaller incision is made over the kneecap.
- Implantation: The damaged surfaces of the kneecap are replaced.
Risks
- Limited Relief: May not relieve pain for all patients.
- Infection: Risk of infection is always present.
- Instability: Some patients may experience instability post-surgery.
Robot-Assisted Knee Replacement
Robot-assisted knee replacement uses advanced technology to enhance the precision of the surgery. This modern approach falls under the types of knee replacement surgery and offers unique benefits. Here’s an overview:
- Benefits: Enhanced precision can lead to better alignment and potentially faster recovery.
- Indications: Suitable for patients undergoing total or partial knee replacement.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: General or spinal anesthesia is used.
- Robotic Guidance: Surgeons use robotic systems for precise cuts and placement.
- Joint Replacement: The surgery proceeds as a typical knee replacement but with robotic assistance.
Risks
- Technology Dependence: Reliant on technology, which may pose issues if malfunction occurs.
- Cost: May be more expensive than traditional methods.
- Learning Curve: Surgeons must be trained in robotic techniques.
Benefits of Knee Surgery
Knee replacement surgery can lead to life-changing benefits, allowing patients to regain independence and live pain-free. Some benefits include:
- Pain Relief: Surgery relieves chronic knee pain that limits daily activities.
- Enhanced Mobility: Replacing the damaged joint allows smoother, pain-free movement.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients regain the ability to walk, exercise, and engage in daily activities.
- Long-Lasting Solution: Many modern knee replacements last up to 15-20 years, especially with new techniques and materials.
The right types of knee replacement surgery can bring a return to daily life without pain or mobility restrictions.
Risks of Knee Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, like any major procedure, carries certain risks that patients should be aware of. Common risks include infection, blood clots, implant loosening, or stiffness in the joint. The likelihood and severity of complications depend on the patient’s health, age, and the types of knee replacement surgery performed. Proper pre-operative evaluation, skilled surgical techniques, and post-operative care can significantly reduce these risks. Consulting an experienced orthopedic surgeon ensures safer outcomes and faster recovery.
- Infection: In rare cases, the surgical site may become infected.
- Blood Clots: Post-surgical blood clots are possible, particularly in the legs.
- Tissue and Nerve Damage: There may be some minor nerve or tissue damage in the surrounding area.
- Knee Stiffness: A small percentage of patients experience stiffness or limited flexibility after surgery.
Discussing these risks with your doctor can help you weigh the benefits against the potential downsides of each procedure.
How do I know if I need knee replacement surgery?
Knowing when you might need knee replacement surgery depends on the severity of your pain and how much it affects your daily life. If walking, climbing stairs, or even resting becomes difficult due to stiffness or swelling, it may be time to consider surgical options. Consulting an orthopedic specialist can help determine if a new type of knee replacement is suitable for your condition. Persistent pain despite medication or physiotherapy is often a strong indicator for knee replacement surgery.
Tips for Preparing for Knee Replacement Surgery
Preparation is key to a successful surgery and smooth recovery. Here are some practical steps to take before surgery:
- Build Leg and Core Strength: Exercise can help make post-surgery physical therapy easier.
- Plan Your Living Space: Prepare your home for easy accessibility, especially if you’ll be on crutches or using a walker.
- Arrange Support: Having a family member or friend to assist with daily activities can reduce stress during recovery.
- Diet Adjustments: Eating a balanced, nutrient-rich diet can aid in faster healing and improve overall recovery.
These steps are simple but can make a big difference in reducing stress and speeding up recovery.
What to Expect After Knee Surgery
After knee surgery, patients can expect to spend several days in the hospital, followed by ongoing rehabilitation at home or at a rehabilitation center. Recovery typically includes:
- Physical Therapy: Therapy starts soon after surgery to help regain knee function.
- Pain Management: Medications and other pain management techniques are often prescribed.
- Gradual Mobility: Patients will gradually regain mobility, moving from crutches or walkers to unaided walking.
- Regular Check-ups: Follow-up visits ensure recovery is on track.
A successful recovery often means returning to a more active life, but following your physical therapy plan is essential.
When You Go Home to Heal
At home, continue to practice the physical therapy exercises and take care of your incision site to prevent infection. Some tips for a smooth recovery at home include:
- Exercise Consistently: Light, doctor-approved exercises keep your muscles strong.
- Prevent Falls: Keep your living area clutter-free to avoid tripping.
- Follow Your Doctor’s Plan: Avoid excessive bending, kneeling, or strenuous activities early on.
- Seek Support: Having help for daily activities, cooking, or running errands can be beneficial.
A strong support system at home helps patients focus on healing and prevents setbacks.
Conclusion
With various types of knee replacement surgery available, patients can choose treatments suited to their individual needs and conditions. Each procedure—whether partial, total, or minimally invasive—offers unique benefits for restoring mobility and relieving pain. Consulting an expert ensures the best choice for your lifestyle and recovery goals. Dr. Madan Mohan Reddy and Dr. Karthik Reddy P are among the best for knee replacement in Chennai, offering advanced techniques and compassionate care for long-lasting, pain-free movement.
